Last Updated on September 20, 2023 by Larious
Summarize this content to 100 words Android has made big improvements in its file management system and app efficiency. However, with larger operating system files, heavier apps, and resource-consuming games, Android devices can quickly fill up despite having large storage capacities. Apart from easily identifiable files like photos, videos, apps, and games, there’s a category called “Other” that includes unidentified storage files. In this article, we’ll show you how to get rid of the files from the “Other” category and free up more storage space on your Android. What Is “Other” Storage on Android? In Android devices, the “Other” category refers to the storage space that is not specifically categorized under identifiable files like photos, videos, apps, or games. It includes various types of files that are not easily recognized by the system and fall into a miscellaneous or uncategorized group. These files might include: Private App Data. Some Android apps and games create data that doesn’t fit into the standard categories, such as additional downloaded files, cloud sync data, and temporary files from streaming services. Failed Backups. Cloud backup services may encounter issues during backup, resulting in incomplete or failed backups, which end up in the “Other” section. Failed OTA Updates. Over-the-air updates can sometimes fail due to poor network conditions or other reasons, leaving behind temporary installer files in the “Other” storage. Hidden Cache Files & Temporary Data. Apps and games download temporary data files like images, videos, and text, which might not always get cleared properly, leading to their accumulation in the “Other” category. Miscellaneous System Files. Some system files and data that don’t fit into standard categories may also contribute to the “Other” storage. The “Other” storage is often a mix of various files that don’t have a clear distinction, making it challenging to identify and manage them individually. As a result, this category may grow over time, taking up valuable storage space on the device. Cleaning up the “Other” storage can help free up space and improve the overall performance of your Android device. How to Clean Up Other Storage and Free Up Storage Space on Android There are different methods you can use to clean up the “Other” section in your Android device’s internal memory. You can try the following techniques one by one until you’re happy with the freed-up internal storage on your Android phone. 1. Use the Clean-Up Feature on Your Android Most Android devices now offer a convenient Clean up feature within the Settings app, allowing you to easily free up your phone’s internal storage. To use the Clean up feature on your smartphone, follow the steps below. Please note that the appearance and location of the Clean up feature might vary slightly depending on your device’s manufacturer and Android version. On your smartphone, open Settings. Inside the Settings app, scroll down until you find the Storage option. For Samsung devices, phone storage may be labeled as Device Care. If you have difficulty finding it, simply use the search bar at the top and type in Storage. Select Storage, and you’ll be presented with a breakdown of different categories, such as Photos, Videos, Other Media Files, Apps, Games, and more. You can select any of these categories to see more information about its contents. Within each category, you can identify files that are consuming space and decide which ones to delete. Tap on individual files or select multiple files to remove them from your device. While the Clean Up feature doesn’t allow you to remove the files from the Other category specifically, you can use it to perform a deep cleanup of your phone and free up a lot of space on your Android. The Clean Up option helps you efficiently manage your Android storage by identifying and removing unnecessary files. Some Android phone models also have the Clean storage option, which you can access by swiping down on the home screen. You’ll see the feature in the drop-down menu above the notification bar. 2. Clean Up Data Used by Proprietary Apps Your Android device’s storage may be filling up due to app data, like hidden cached data, temporary files, as well as additional downloaded files. Luckily, Android devices have another built-in function to help you manage these large files – a memory scanner that can help you clean up the cache. To clean up this data, follow the steps below. Open the phone’s Settings app. Navigate to the Storage Options section if applicable, or go to Storage > Apps. If your device allows, sort the apps based on their size. If not, manually check each app to find the ones with large data sizes. Open the app you want to manage (one that’s taking up a lot of storage space) and select the Clear Cache option. If clearing the app cache doesn’t free up enough space, you can try tapping Clear Data. Please note that selecting Clear Data will remove all app data, and you may need to log in again and download additional data that was needed during the initial installation. This option should be used with caution, as it may result in loss of app settings and preferences. 3. Clean Up Android/obb & Android/data Directories When you uninstall apps from your device, sometimes their files are not completely removed from the system. This can happen because of certain issues with updates that are not compatible with the app, or it can be caused by third-party launchers that are not fully optimized for your specific device. As a result, some app files may remain in your device’s storage even after you have deleted the app. If you have already tried the previous methods to clear the Other storage and it didn’t work, you can try this method to manually clean up leftover app files from deleted apps in your local storage. Here’s how you can do it. Open your preferred File Manager app. Go to the Settings section of the File Manager and enable the option to Show System Files & Folders or Display hidden files. Navigate to the /Android/obb directory in your file manager. In this directory, most files will have names like com.ABC.XYZ, where ABC represents the developer name, and XYZ represents the app name. Look through this section to find names of apps that you have previously deleted. If you find any, go ahead and delete them. After you’re done with the /Android/obb directory, navigate to the /Android/data directory. Follow the same steps as before to identify leftover data from deleted apps. Delete any files related to apps you no longer use. Finally, check your Other storage to see if the space has been freed up. By manually cleaning up these directories, you may be able to clear up some storage space that was occupied by leftover files from previously deleted apps. 4. Clear Android Cache in Recovery Mode You can also attempt to clear the Other storage category by clearing your user interface (UI) cache in Recovery Mode. You can use our comprehensive guide on How to Boot Into & Use Recovery Mode on Android to learn how to do it. Please note that Recovery Mode is a sensitive menu, and making the wrong changes can potentially harm your Android device. Be cautious and proceed only if you feel confident in your technical abilities. If you are unsure, consider trying the next solution instead. 5. Return to the Original Stock ROM If you have installed a custom ROM on your rooted device, there is a possibility that the custom ROM might have some glitches. Some major custom ROMs like Lineage OS, Pixel OS, and others have experienced issues where the file system duplicates itself, leading to storage space clogs and unidentified files in the Other section of the memory scanner. If the previously mentioned solutions do not work, a good option to fix this problem is to go back to the stock ROM, which is the original operating system that came with your device. You can wait for an update from the developer of the custom ROM to fix the issue. Additionally, you can also reach out for help by submitting a request on the developer’s Github account, especially if they are actively involved and responsive to bug reports. 6. Factory Reset Your Android Smartphone If all else fails, consider resetting your device to its original factory settings. This can help improve the phone’s speed…
Android has made big improvements in its file management system and app efficiency. However, with larger operating system files, heavier apps, and resource-consuming games, Android devices can quickly fill up despite having large storage capacities. Apart from easily identifiable files like photos, videos, apps, and games, there’s a category called “Other” that includes unidentified storage files.
In this article, we’ll show you how to get rid of the files from the “Other” category and free up more storage space on your Android.
Table of Contents
What Is “Other” Storage on Android?
In Android devices, the “Other” category refers to the storage space that is not specifically categorized under identifiable files like photos, videos, apps, or games. It includes various types of files that are not easily recognized by the system and fall into a miscellaneous or uncategorized group.
These files might include:
- Private App Data. Some Android apps and games create data that doesn’t fit into the standard categories, such as additional downloaded files, cloud sync data, and temporary files from streaming services.
- Failed Backups. Cloud backup services may encounter issues during backup, resulting in incomplete or failed backups, which end up in the “Other” section.
- Failed OTA Updates. Over-the-air updates can sometimes fail due to poor network conditions or other reasons, leaving behind temporary installer files in the “Other” storage.
- Hidden Cache Files & Temporary Data. Apps and games download temporary data files like images, videos, and text, which might not always get cleared properly, leading to their accumulation in the “Other” category.
- Miscellaneous System Files. Some system files and data that don’t fit into standard categories may also contribute to the “Other” storage.
The “Other” storage is often a mix of various files that don’t have a clear distinction, making it challenging to identify and manage them individually. As a result, this category may grow over time, taking up valuable storage space on the device. Cleaning up the “Other” storage can help free up space and improve the overall performance of your Android device.
How to Clean Up Other Storage and Free Up Storage Space on Android
There are different methods you can use to clean up the “Other” section in your Android device’s internal memory. You can try the following techniques one by one until you’re happy with the freed-up internal storage on your Android phone.
1. Use the Clean-Up Feature on Your Android
Most Android devices now offer a convenient Clean up feature within the Settings app, allowing you to easily free up your phone’s internal storage.
To use the Clean up feature on your smartphone, follow the steps below. Please note that the appearance and location of the Clean up feature might vary slightly depending on your device’s manufacturer and Android version.
- On your smartphone, open Settings.
- Inside the Settings app, scroll down until you find the Storage option. For Samsung devices, phone storage may be labeled as Device Care. If you have difficulty finding it, simply use the search bar at the top and type in Storage.
- Select Storage, and you’ll be presented with a breakdown of different categories, such as Photos, Videos, Other Media Files, Apps, Games, and more. You can select any of these categories to see more information about its contents.

- Within each category, you can identify files that are consuming space and decide which ones to delete. Tap on individual files or select multiple files to remove them from your device.
- While the Clean Up feature doesn’t allow you to remove the files from the Other category specifically, you can use it to perform a deep cleanup of your phone and free up a lot of space on your Android.

The Clean Up option helps you efficiently manage your Android storage by identifying and removing unnecessary files.
Some Android phone models also have the Clean storage option, which you can access by swiping down on the home screen. You’ll see the feature in the drop-down menu above the notification bar.

2. Clean Up Data Used by Proprietary Apps
Your Android device’s storage may be filling up due to app data, like hidden cached data, temporary files, as well as additional downloaded files. Luckily, Android devices have another built-in function to help you manage these large files – a memory scanner that can help you clean up the cache.
To clean up this data, follow the steps below.
- Open the phone’s Settings app.
- Navigate to the Storage Options section if applicable, or go to Storage > Apps.
- If your device allows, sort the apps based on their size. If not, manually check each app to find the ones with large data sizes.

- Open the app you want to manage (one that’s taking up a lot of storage space) and select the Clear Cache option.

If clearing the app cache doesn’t free up enough space, you can try tapping Clear Data.
Please note that selecting Clear Data will remove all app data, and you may need to log in again and download additional data that was needed during the initial installation. This option should be used with caution, as it may result in loss of app settings and preferences.
3. Clean Up Android/obb & Android/data Directories
When you uninstall apps from your device, sometimes their files are not completely removed from the system. This can happen because of certain issues with updates that are not compatible with the app, or it can be caused by third-party launchers that are not fully optimized for your specific device. As a result, some app files may remain in your device’s storage even after you have deleted the app.
If you have already tried the previous methods to clear the Other storage and it didn’t work, you can try this method to manually clean up leftover app files from deleted apps in your local storage.
Here’s how you can do it.
- Open your preferred File Manager app.
- Go to the Settings section of the File Manager and enable the option to Show System Files & Folders or Display hidden files.

- Navigate to the /Android/obb directory in your file manager. In this directory, most files will have names like com.ABC.XYZ, where ABC represents the developer name, and XYZ represents the app name.
- Look through this section to find names of apps that you have previously deleted. If you find any, go ahead and delete them.
- After you’re done with the /Android/obb directory, navigate to the /Android/data directory.
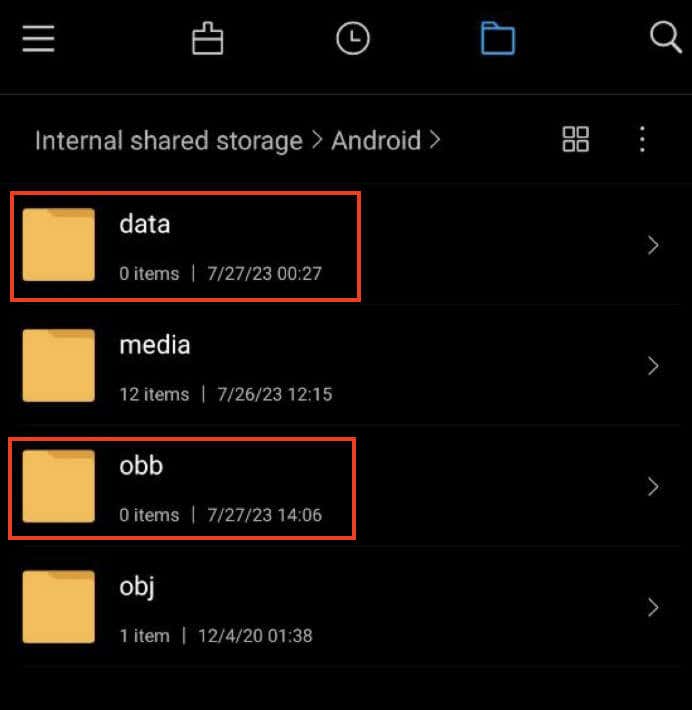
- Follow the same steps as before to identify leftover data from deleted apps. Delete any files related to apps you no longer use.
Finally, check your Other storage to see if the space has been freed up.
By manually cleaning up these directories, you may be able to clear up some storage space that was occupied by leftover files from previously deleted apps.
4. Clear Android Cache in Recovery Mode
You can also attempt to clear the Other storage category by clearing your user interface (UI) cache in Recovery Mode. You can use our comprehensive guide on How to Boot Into & Use Recovery Mode on Android to learn how to do it.
Please note that Recovery Mode is a sensitive menu, and making the wrong changes can potentially harm your Android device. Be cautious and proceed only if you feel confident in your technical abilities. If you are unsure, consider trying the next solution instead.
5. Return to the Original Stock ROM
If you have installed a custom ROM on your rooted device, there is a possibility that the custom ROM might have some glitches. Some major custom ROMs like Lineage OS, Pixel OS, and others have experienced issues where the file system duplicates itself, leading to storage space clogs and unidentified files in the Other section of the memory scanner.
If the previously mentioned solutions do not work, a good option to fix this problem is to go back to the stock ROM, which is the original operating system that came with your device. You can wait for an update from the developer of the custom ROM to fix the issue.
Additionally, you can also reach out for help by submitting a request on the developer’s Github account, especially if they are actively involved and responsive to bug reports.
6. Factory Reset Your Android Smartphone
If all else fails, consider resetting your device to its original factory settings. This can help improve the phone’s speed and give you a fresh start by clearing up storage issues.
Before proceeding with the reset, make sure to back up your device properly. You can back up your data to Google Drive, and Samsung devices have a feature called Smart Switch for backup.
Here’s how to perform a factory reset on your Android.
- Open the Settings app on your device.
- Use the search bar at the top to find the Factory reset or Reset phone option.
- Select this option to confirm.
Follow the on-screen instructions to perform the factory reset, which may vary depending on your phone’s user interface. After the reset, selectively restore your data back to your device and keep an eye on your device storage.
7. Use an External Storage Device
If the previous methods did not work to clear the Other storage section on your device, you may need to take more drastic measures to solve the issue. One option is to move your data to an SD card and then reset your phone.

Before you do that, we recommend backing up your data to Google Drive or other cloud storage to avoid losing any important information.
To move your data to an SD card, follow the steps below.
- Insert a high-capacity SD card into your device. If your device doesn’t have an SD card slot, you can use an OTG card reader.
- Create a manual backup of all your important data files.
- Back up your contacts and saved passwords onto the SD card.
- Reset your device to its factory settings.
Set up your device as new and restore your files and local contacts backup from the SD card. By following these steps, your Other storage should be cleared, and your device should return to normal.
8. Use a Third-Party App to Clean Up Your Other Storage
Finally, if you don’t want to go through the hassle of trying different methods to clean up your storage, try using a Storage Analyzer or File Manager app to gain a better understanding of your storage and disk usage. With an efficient file manager, you can easily examine the larger files stored on your device.
These apps allow you to sort files by size, making it easier to identify large files that may be contributing to the Other data. Additionally, you can view system files and hidden files on your local storage, which could be the main cause of the large amount of Other data. You can consult our comparison piece on the Best File Manager Apps for Android and take your pick of the app on Google Play Store.
Take a Smart Approach to Managing Your Android Storage
Managing Other storage on your Android device is crucial for optimizing performance and freeing up space. By regularly clearing cache, app data and using storage analyzer apps, you can identify and remove unnecessary files.
Be cautious when using more drastic measures like factory resetting, as they may lead to data loss. Taking proactive steps to clean up Other storage will result in a smoother and more efficient Android experience, with more available storage for your needs.
conclusion Android has made big improvements in its file management system and app efficiency. However, with larger operating system files, heavier apps, and resource-consuming games, Android devices can quickly fill up despite having large storage capacities. Apart from easily identifiable files like photos, videos, apps, and games, there’s a category called “Other” that includes unidentified storage files. In this article, we’ll show you how to get rid of the files from the “Other” category and free up more storage space on your Android. What Is “Other” Storage on Android? In Android devices, the “Other” category refers to the storage space that is not specifically categorized under identifiable files like photos, videos, apps, or games. It includes various types of files that are not easily recognized by the system and fall into a miscellaneous or uncategorized group. These files might include: Private App Data. Some Android apps and games create data that doesn’t fit into the standard categories, such as additional downloaded files, cloud sync data, and temporary files from streaming services. Failed Backups. Cloud backup services may encounter issues during backup, resulting in incomplete or failed backups, which end up in the “Other” section. Failed OTA Updates. Over-the-air updates can sometimes fail due to poor network conditions or other reasons, leaving behind temporary installer files in the “Other” storage. Hidden Cache Files & Temporary Data. Apps and games download temporary data files like images, videos, and text, which might not always get cleared properly, leading to their accumulation in the “Other” category. Miscellaneous System Files. Some system files and data that don’t fit into standard categories may also contribute to the “Other” storage. The “Other” storage is often a mix of various files that don’t have a clear distinction, making it challenging to identify and manage them individually. As a result, this category may grow over time, taking up valuable storage space on the device. Cleaning up the “Other” storage can help free up space and improve the overall performance of your Android device. How to Clean Up Other Storage and Free Up Storage Space on Android There are different methods you can use to clean up the “Other” section in your Android device’s internal memory. You can try the following techniques one by one until you’re happy with the freed-up internal storage on your Android phone. 1. Use the Clean-Up Feature on Your Android Most Android devices now offer a convenient Clean up feature within the Settings app, allowing you to easily free up your phone’s internal storage. To use the Clean up feature on your smartphone, follow the steps below. Please note that the appearance and location of the Clean up feature might vary slightly depending on your device’s manufacturer and Android version. On your smartphone, open Settings. Inside the Settings app, scroll down until you find the Storage option. For Samsung devices, phone storage may be labeled as Device Care. If you have difficulty finding it, simply use the search bar at the top and type in Storage. Select Storage, and you’ll be presented with a breakdown of different categories, such as Photos, Videos, Other Media Files, Apps, Games, and more. You can select any of these categories to see more information about its contents. Within each category, you can identify files that are consuming space and decide which ones to delete. Tap on individual files or select multiple files to remove them from your device. While the Clean Up feature doesn’t allow you to remove the files from the Other category specifically, you can use it to perform a deep cleanup of your phone and free up a lot of space on your Android. The Clean Up option helps you efficiently manage your Android storage by identifying and removing unnecessary files. Some Android phone models also have the Clean storage option, which you can access by swiping down on the home screen. You’ll see the feature in the drop-down menu above the notification bar. 2. Clean Up Data Used by Proprietary Apps Your Android device’s storage may be filling up due to app data, like hidden cached data, temporary files, as well as additional downloaded files. Luckily, Android devices have another built-in function to help you manage these large files – a memory scanner that can help you clean up the cache. To clean up this data, follow the steps below. Open the phone’s Settings app. Navigate to the Storage Options section if applicable, or go to Storage > Apps. If your device allows, sort the apps based on their size. If not, manually check each app to find the ones with large data sizes. Open the app you want to manage (one that’s taking up a lot of storage space) and select the Clear Cache option. If clearing the app cache doesn’t free up enough space, you can try tapping Clear Data. Please note that selecting Clear Data will remove all app data, and you may need to log in again and download additional data that was needed during the initial installation. This option should be used with caution, as it may result in loss of app settings and preferences. 3. Clean Up Android/obb & Android/data Directories When you uninstall apps from your device, sometimes their files are not completely removed from the system. This can happen because of certain issues with updates that are not compatible with the app, or it can be caused by third-party launchers that are not fully optimized for your specific device. As a result, some app files may remain in your device’s storage even after you have deleted the app. If you have already tried the previous methods to clear the Other storage and it didn’t work, you can try this method to manually clean up leftover app files from deleted apps in your local storage. Here’s how you can do it. Open your preferred File Manager app. Go to the Settings section of the File Manager and enable the option to Show System Files & Folders or Display hidden files. Navigate to the /Android/obb directory in your file manager. In this directory, most files will have names like com.ABC.XYZ, where ABC represents the developer name, and XYZ represents the app name. Look through this section to find names of apps that you have previously deleted. If you find any, go ahead and delete them. After you’re done with the /Android/obb directory, navigate to the /Android/data directory. Follow the same steps as before to identify leftover data from deleted apps. Delete any files related to apps you no longer use. Finally, check your Other storage to see if the space has been freed up. By manually cleaning up these directories, you may be able to clear up some storage space that was occupied by leftover files from previously deleted apps. 4. Clear Android Cache in Recovery Mode You can also attempt to clear the Other storage category by clearing your user interface (UI) cache in Recovery Mode. You can use our comprehensive guide on How to Boot Into & Use Recovery Mode on Android to learn how to do it. Please note that Recovery Mode is a sensitive menu, and making the wrong changes can potentially harm your Android device. Be cautious and proceed only if you feel confident in your technical abilities. If you are unsure, consider trying the next solution instead. 5. Return to the Original Stock ROM If you have installed a custom ROM on your rooted device, there is a possibility that the custom ROM might have some glitches. Some major custom ROMs like Lineage OS, Pixel OS, and others have experienced issues where the file system duplicates itself, leading to storage space clogs and unidentified files in the Other section of the memory scanner. If the previously mentioned solutions do not work, a good option to fix this problem is to go back to the stock ROM, which is the original operating system that came with your device. You can wait for an update from the developer of the custom ROM to fix the issue. Additionally, you can also reach out for help by submitting a request on the developer’s Github account, especially if they are actively involved and responsive to bug reports. 6. Factory Reset Your Android Smartphone If all else fails, consider resetting your device to its original factory settings. This can help improve the phone’s speed and give you a fresh…
